trachea
(redirected from tracheae)Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia.
tra·che·a
(trā′kē-ə)n. pl. tra·che·ae (-kē-ē′) or tra·che·as
1. Anatomy A thin-walled, cartilaginous tube descending from the larynx to the bronchi and carrying air to the lungs. Also called windpipe.
2. Zoology One of the internal respiratory tubes of insects and some other terrestrial arthropods, which are connected to the spiracles and are used for gas exchange.
3. Botany A tracheary element.
[Middle English trache, from Medieval Latin trāchēa, from Late Latin trāchīa, from Greek (artēriā) trākheia, rough (artery), trachea (as opposed to the smooth vessels that carry blood and not air), feminine of trākhus, rough.]
tra′che·al adj.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
trachea
(trəˈkiːə)n, pl -cheae (-ˈkiːiː)
1. (Anatomy) anatomy zoology the membranous tube with cartilaginous rings that conveys inhaled air from the larynx to the bronchi. Nontechnical name: windpipe
2. (Zoology) any of the tubes in insects and related animals that convey air from the spiracles to the tissues
[C16: from Medieval Latin, from Greek trakheia, shortened from (artēria) trakheia rough (artery), from trakhus rough]
traˈcheal, traˈcheate, tracheated adj
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
tra•che•a
(ˈtreɪ ki ə)n., pl. -che•ae (-kiˌi) -che•as.
1. (in air-breathing vertebrates) a tube that extends from the larynx to the bronchi, serving as the principal passageway of air to and from the lungs; windpipe.
2. (in insects and certain other invertebrates) any of a network of air-conveying tubules throughout the body.
[1350–1400; Middle English trache < Medieval Latin trāchēa, for Late Latin trāchīa < Greek trācheîa, short for artēría trācheîa rough artery, i.e., windpipe]
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
tra·che·a
(trā′kē-ə)1. The tube-shaped structure in vertebrate animals that leads from the larynx to the bronchi and carries air to the lungs. In mammals, the trachea is strengthened by rings of cartilage. Also called windpipe.
2. A similar structure in insects and other arthropods.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
trachea
(or windpipe) The tube between the larynx and the bronchi.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | 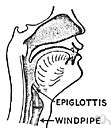 trachea - membranous tube with cartilaginous rings that conveys inhaled air from the larynx to the bronchi trachea - membranous tube with cartilaginous rings that conveys inhaled air from the larynx to the bronchiepiglottis - a flap of cartilage that covers the windpipe while swallowing upper respiratory tract - the nose and throat and trachea cartilaginous tube - a duct with cartilaginous walls |
| 2. |  trachea - one of the tubules forming the respiratory system of most insects and many arachnids trachea - one of the tubules forming the respiratory system of most insects and many arachnidstubule - a small tube respiratory system, systema respiratorium - the system for taking in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide; in terrestrial animals this is accomplished by breathing |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Translations
průdušnice
Trachea
henkitorvi
dušnik
trachee
sapnik
Collins Spanish Dictionary - Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
trachea
n → Luftröhre f; (of insects) → Trachea f
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
tra·che·a
n. tráquea, conducto respiratorio entre la parte extrema inferior de la laringe y el comienzo de los bronquios.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
trachea
n (pl -cheae o -cheas) tráqueaEnglish-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.